
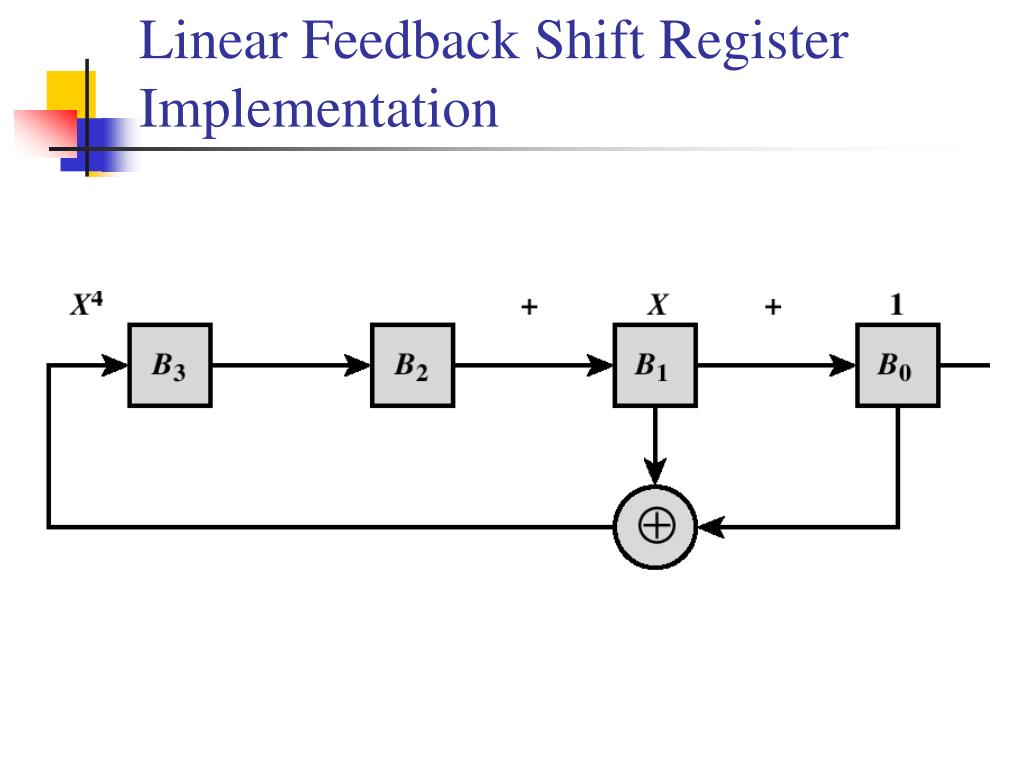
For linear congruential generators (LCGs) failure can be shown theoretically. The expectation time that a repetition occurs provides the metric for the test. The idea is that a sequence of pseudo-random numbers should have numbers reappear with a certain probability. Petersen, Wesley P.Ī new statistical test for uniform pseudo-random number generators (PRNGs) is presented. In this article the test results of RNG correlation, speed and identity of computations for PC, Sun4 and VAX computer tests are presentedĪ Repetition Test for Pseudo-Random Number Generators In this random number generator the repetition period is about 10 36 what should be sufficient for all computers in the world. The pseudo-random number generator (RNG) was written to match needs of nuclear and high-energy physics computation which in some cases require very long and independent random number sequences. The exponentiator in GF(2 sup m) is novel and comprises a cyclic-shift circuit a Massey-Omura multiplier and, a control logic circuit all operably connected together to perform the function U(sub i) = 92(sup i) (for n(sub i) = 1 or 1 (for n(subi) = 0). Whereby after the exponentiator initially receives the primitive element (A sub O) in GF(2 sup m) through the switch, the switch can be switched to cause the exponentiator to receive as its input a delayed output A(K-1) from the exponentiator thereby generating (A sub K) continuously at the output of the exponentiator. The delay circuit output is connected to the other of the switch inputs and the delay circuit input is connected to the output of the exponentiator. Finally, there is a delay circuit having an input and an output. One of the switch inputs is connected for initially receiving a primitive element (A sub O) in GF(2 sup m). The switch outputs is connected to the other of the two inputs of the exponentiator. There is a switch having a pair of inputs and an output.

One of the two inputs is connected to receive the outputs (E sub K) of maximal length shift register of n stages. There is an exponentiator in GF(2 sup m) for the normal basis representation of elements in a finite field GF(2 sup m) each represented by m binary digits and having two inputs and an output from which the sequence (A sub K). Long period pseudo random number sequence generatorĪ circuit for generating a sequence of pseudo random numbers, (A sub K). The parameters of these planes are obtained for three random number generators. This effect should be taken into account in Monte-Carlo calculations with definite constructive dimension. International Nuclear Information System (INIS)Īn algorithm is suggested for searching with a computer in unit n-dimensional cube the sets of planes where all the points fall whose coordinates are composed of n successive pseudo-random numbers of multiplicative sequence.
Correlations of pseudo-random numbers of multiplicative sequence


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
